Surface Condensers
The surface condensers are of two types :
(I) Surface condensers : In this the steam flows outside the network of tubes and we flows inside the tubes.
(II) Evaporative condensers : In this the condenser shell is omitted. The steam puses through condenser tubes and over these tubes the water is sprayed while the air passes upwards outside the tube. The surface condenser are further classified based on
(a) The number of water passes Single pass or multipass
(b) The direction of condensate flow and tube arrangement e.g. down flow condenser, central flow condenser etc.
Double Pass Surface Condenser :
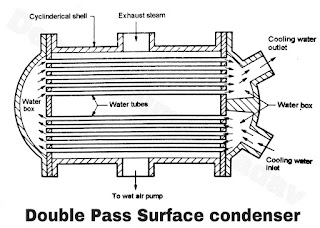
- A schematic diagram of a double pass surface condenser is shown in Figure A. It consists of cast iron cylindrical shell which is made airtight and it is closed at each end as shown in Figure A.
- A water circulating pump is used to circulate the cooling water into the condenser. This water enters at one end of the lower half of the tubes, flows to the other end and again it returns through the upper half of the tubes as shown by arrowheads.
- The exhaust steam enters at the top of the condenser and while it flows down over the tubes, the steam gets condensed. The condensate with air is extract with the help of wet air pump from the bottom side of the condenser as shown in Figure A.
- The condenser tubes are usually made of red brass in case the cooling water used is impure.
- In some condensers, we employ two pumps separately for extraction of condensate and for the air. The pumps employed are usually centrifugal type, however, at times the steam ejectors are used for air removal.
 |
| Figure A |
Down Flow Surface Condenser :
- The cross-section of another types of condenser called down flow surface condenser is shown in Figure B.
- The working principle is similar to double pass surface condenser except that this condenser employs two separate pumps for the extraction of condensate and the air.
- Baffles are provided so that the air is cooled to the minimum temperature before it is extracted.
- Due to the cooling of air, its specific volume reduces, thereby, it reduces the pump capacity to about 50%. Therefore, it also reduces the energy consumption for running the air pump.
 |
| Figure B |
- The cross-section of a central flow condenser is shown in Figure C.
- In this type of condenser, the suction of the air extraction pump is located at the centre of the condenser tubes due to which the steam flows radially inwards as shown by arrowhead.
- The steam after condensation is extracted from the bottom of the condenser with the help of condensate extraction pump.
- This type of condenser provides the better contact of steam with the tubes all around its periphery compared to downward flow condenser.
 |
| Figure C |